Modern games are massive. Some titles take over 100 gigabytes of space. Gamers deal with slow downloads, long load times, and full hard drives. Developers struggle with storage demands and performance balance. Cloud gaming adds more pressure to store data efficiently.
Game studios, cloud platforms, and engine builders need smart ways to save space. One powerful solution is called a single instance store. It may sound technical, but it plays a big role in how your game runs.
This system keeps only one copy of each file or object, no matter how many times it’s used. That sounds simple, but it changes everything. It improves load speed, saves memory, and supports faster game updates.
In this guide, you will learn how single instance storage works, why it matters, and how it shapes the future of gaming. Whether you play games or build them, this is a core idea you need to understand.
What Does “Single Instance Store” Mean?
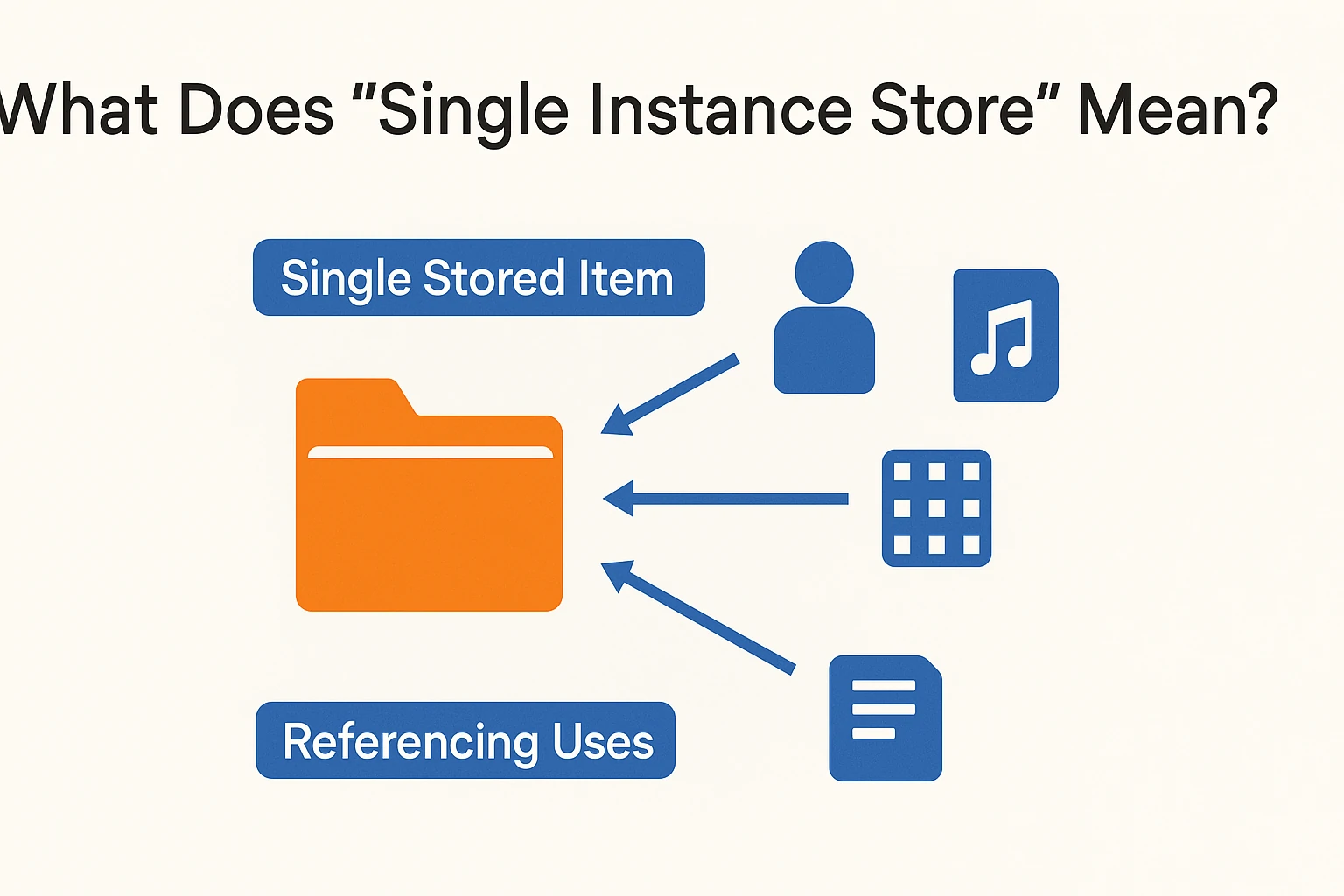
A single instance store keeps only one version of a file, texture, sound, or object. Even if a game uses the same file many times, it does not copy it over and over.
Instead, the system points each use back to that single stored item. The game engine pulls from that source every time. That means less storage is needed and less data gets repeated.
This storage model also makes patching easier. If a shared file needs changes, developers update one version. The whole game reflects that change without bloating the file size.
The idea is common in software, cloud servers, and databases. In gaming, it helps manage assets like:
- Character models used across many levels
- Sounds reused in different maps
- Large textures applied to multiple areas
- Game logic or code blocks repeated in scenes
When every part links back to one source, the game becomes leaner and smarter.
Why Modern Games Rely on Smart Storage

Games have changed over the last 20 years. In the past, a title came on one CD. Today, players need terabytes of storage to install full libraries.
This growth comes from:
- 4K textures
- Advanced physics engines
- Large open worlds
- Voice packs and music
- Real-time online systems
Without smart storage models, these features would crash systems or delay updates for hours.
Developers now use single instance stores to:
- Cut download times
- Improve patch delivery
- Keep disk space low
- Increase speed on loading assets
- Avoid crashes from redundant memory use
This tech is not optional anymore. It’s required to build games at scale.
How Much Power Does Your PC Use? Cut Costs with These Smart Tips
The Evolution of Game Storage: From CDs to Smart File Linking
Game storage has come a long way. Early titles fit on floppy disks or CDs. Developers used small assets. Games loaded from local drives. No internet connection was required.
Over time, file sizes grew. DVDs and Blu-rays allowed more data. Studios added better textures, audio, and voice packs. Load times increased. Patches took hours.
As online gaming grew, so did update demands. Players needed to download full files just to fix small bugs. This made game folders huge and hard to manage.
New methods had to solve this. Systems like single instance storage began to replace old habits. They helped remove duplicate files and link assets from one place. Today’s games rely on this to keep performance high and downloads fast.
Real Examples in AAA Games

Many big titles use this system behind the scenes. You may not see it, but you feel it when the game runs smoothly.
Call of Duty Warzone, for example, has struggled with massive file sizes. Updates once forced players to reinstall large portions of the game. Activision now uses better storage logic, including deduplication and single-instance referencing.
Fortnite uses shared assets across modes. Whether you’re in Battle Royale or Creative mode, the engine pulls from one stored file set.
The Witcher 3 loads the same textures and weather effects across maps. The system avoids repeating files. That’s why open world transitions feel smooth.
Apex Legends and Valorant apply single-instance methods to reduce update sizes and manage character data across patches.
These games run on engines that support single instance logic. Players enjoy faster performance without knowing why.
How Game Engines Use Single Instance Stores
Top game engines are built to support efficient storage. Unity, Unreal Engine, and others use single-instance structures to manage game files.
In Unreal Engine, the Content Browser keeps one file of a mesh or texture. That file can be linked to dozens of actors or blueprints.
In Unity, prefabs help developers reuse objects. The game stores one source file. Every use in the game links back to that. Changes update across all uses instantly.
This method:
- Cuts load time
- Speeds up rendering
- Reduces export file sizes
- Helps with real-time performance
Game engines also support this through internal caching systems. That means textures and models don’t reload from scratch. They pull once and serve as needed.
This improves both dev workflow and player experience.
Behind the Scenes: Why It Works So Well
Single instance storage works better than older systems. The idea seems simple, but the results are powerful. Here are the main reasons:
No Repeated Data
The system does not copy the same file over and over. It saves one version and uses it again. This reduces disk space and cuts memory use.
Central Control
Developers store each file in one place. If they need to fix a problem or change an asset, they do it once. Every part of the game updates from that one change.
Faster Performance
Games load faster when systems do not carry extra copies. One version of each file means less strain. The game runs smoother and crashes less.
Smaller Patches
Updates stay small. If a shared file changes, the game only updates that file. Players spend less time waiting and more time playing.
This system helps developers and players. It keeps games light and fast. It also makes updates easier to manage. The structure is clean and clear. That makes it one of the best choices in game design today.
Single Instance Store in Game Development: Boosting Performance with Smart Storage

Game developers must manage more than just design and graphics. They must control how game data moves, loads, and stores during runtime. The bigger the game, the harder that gets.
A single instance store helps teams handle this challenge. Instead of loading dozens of versions of the same model or sound, the game engine grabs one source and links it across the code. This makes the game lighter and faster.
Developers also reduce errors. They don’t need to update the same file in 10 places. They fix it once, and the change flows across all linked spots. This saves time and avoids bugs.
When creating patches or DLCs, the game only needs to ship new assets, not the reused ones. That speeds up release and cuts download size. In a fast-paced industry, this saves both time and money.
Smart storage also helps with build times. Teams using Unity or Unreal Engine often run batch exports or live builds. Single-instance logic makes that process smoother. Fewer files load. The output compiles faster.
Every hour saved helps meet tight deadlines. This tech gives devs the tools to keep large games running well from start to finish.
How Single Instance Store Helps Indie Devs Build Better Games
Indie developers face tough limits. They often work with small teams and tight budgets. Every file must count. Smart storage helps them build better games without extra cost.
Single instance systems let small studios reuse models, textures, and sounds. They do not need to build the same object many times. This saves memory and keeps projects lean.
Update speed matters too. Indie games often push quick patches. A system that updates one linked file makes that easier. Players get fixes fast without redownloading the game.
Mobile titles and browser games also gain from this. Many platforms have file size limits. Developers meet those limits by storing assets once and linking them across scenes.
This system gives indie teams tools once limited to large studios. It helps them deliver better games with less stress.
Game Engine Storage Optimization: Understanding the Architecture
Modern engines don’t just handle visuals. They act like full platforms. Storage is now a core feature built into their design.
Unreal Engine
Unreal uses asset management tools that support instance referencing. Artists and developers work with one version of a mesh or texture. Levels, NPCs, and environments link back to that version.
Even complex animations or blueprints connect this way. This keeps levels clean and helps reduce memory spikes during runtime.
Unity
Unity’s prefab system also promotes single-instance logic. You create one asset, reuse it everywhere. Change the original, and the rest update.
Scene loading becomes faster. Mobile games or VR titles use this to reduce file size and improve memory use.
Other Custom Engines
Large studios often build their own engines. These systems also follow this pattern. Whether it’s Frostbite (used in Battlefield) or REDengine (from CD Projekt Red), the goal stays the same. Use fewer copies. Share more. Speed up the game.
The architecture often involves asset bundles, memory pools, and reference chains. These may sound complex, but they all aim to support this smart storage model.
Why Modern Games Load Faster: Secrets Behind the Tech
Every player wants fast load times. Nobody wants to sit through long loading screens. Single instance storage helps cut wait time in a few big ways.
Fewer Files to Read
Games often read files during startup or level load. If they can read one shared file instead of 10 copies, the load is faster. The system uses less bandwidth and memory.
Better Memory Management
Storing data once means less RAM use. The engine doesn’t have to unpack and store duplicates. This gives more room for gameplay elements.
Easier Streaming
Some games stream assets as you move. Open-world games do this a lot. With single instance storage, the engine can call one asset from a pool. It doesn’t need to reload the same data each time.
This creates smoother gameplay. You don’t notice textures popping in. Sounds load without delay. Your frame rate stays steady.
Patch Speed
Many players care about update time. Single instance logic helps shrink patch size. That means shorter downloads, faster installs, and less time waiting for gameplay.
Games now use smart tech not just to look good, but to load fast too. Storage is part of that upgrade.
Performance Boosts in Action: Numbers Behind Single Instance Store
Some players want real proof. How much does this storage method help? Let’s look at common results seen in modern engines.
Games using single instance storage cut patch size by up to 60%. Instead of shipping 5GB, studios ship 2GB or less. That saves time for players and money for platforms.
Load speed improves too. Titles with shared file links can load levels 30% faster. This keeps the game moving and avoids long waits.
Memory use drops as well. Reusing one file means less RAM needed. Some games save up to 20% in runtime memory. This helps performance, especially on older systems.
Developers also export builds faster. Unity and Unreal both show 25% shorter build times with smart asset reuse. These numbers show how powerful this method can be.
How to Make a 3rd Person Game in GDevelop: A Simple Guide for you
Single Instance Store vs Traditional Storage in Games: What’s the Real Benefit?
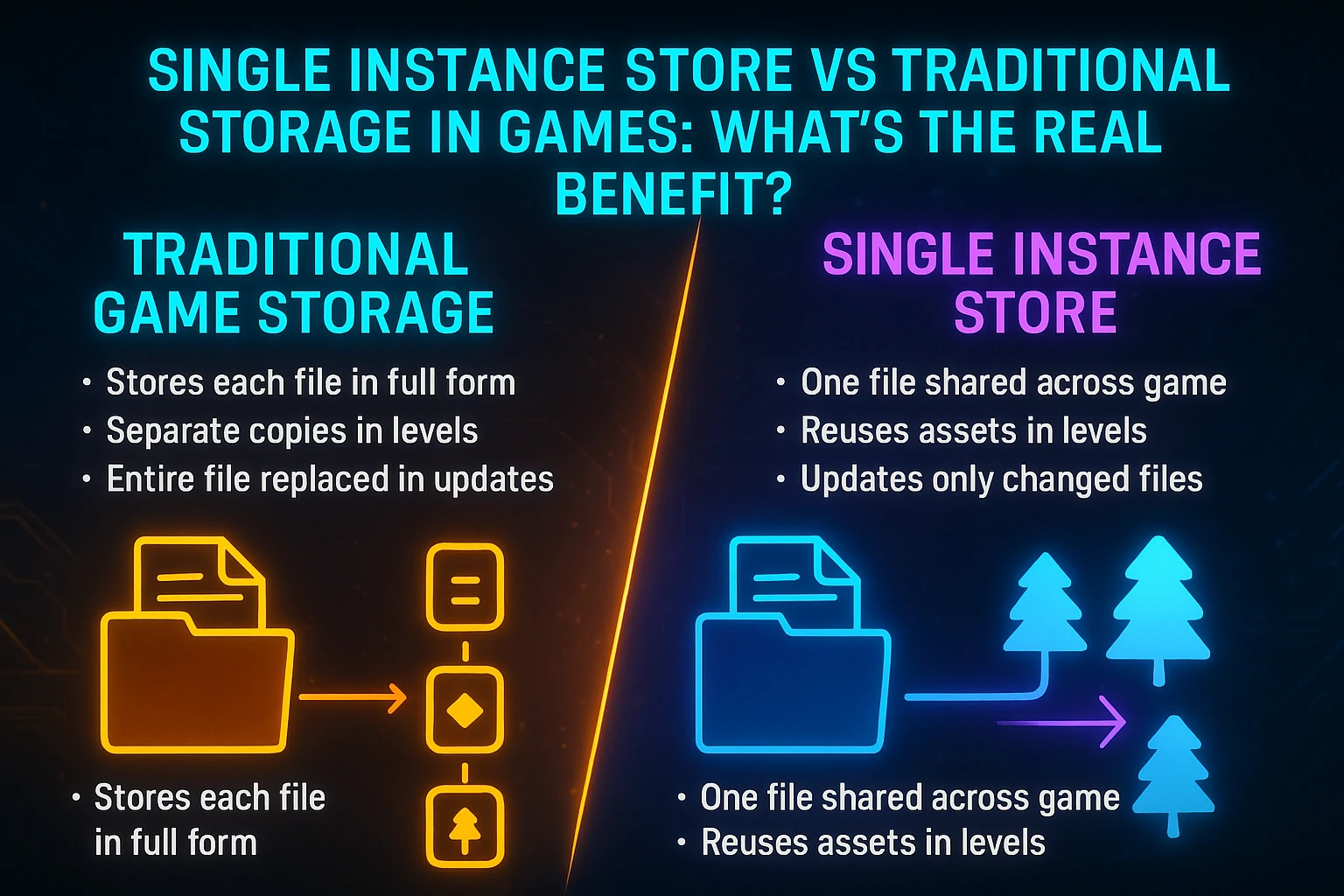
Let’s compare old systems with the new single-instance model.
Traditional Game Storage
Older games stored each file in full form.
Games saved separate copies of textures, models, or sound files.
Each level or scene held its own version.
Patches often replaced entire files, even for small fixes.
This setup worked when games were small.
Today’s games need more.
This old method wastes space.
It slows down performance and creates larger updates.
Single Instance Store
One file links to many parts of the game.
The system shares textures and scripts from a single source.
Levels reuse the same assets.
Patches only update changed files, not full sets.
This method runs faster.
It takes up less space.
It matches the needs of modern games.
Developers and players both gain from this smarter setup.
Here’s a simple example:
Imagine a tree used in 30 places.
Traditional storage keeps 30 tree files.
Single instance storage keeps one and links it 30 times.
That saves memory, disk space, and load time.
The result? Better game builds, smaller downloads, and faster updates.
How It Supports Cloud Gaming and Online Play
Cloud gaming needs fast storage systems. Games run on remote servers. Every second counts. The data must move quickly and stay stable.
Smaller Game Builds
Single instance storage cuts file size. This helps cloud servers run smoother. Small builds load faster and take less space. Players notice shorter wait times.
Quick Data Transfers
Servers send data to users in real time. Fewer files mean faster transfers. One file can support many layers of a game. This avoids delay and keeps gameplay smooth.
Shared Files Across Players
Cloud platforms often host many users in the same space. A single stored file can support all players. That reduces strain on the system. It also saves bandwidth.
Better Sync in Multiplayer
Games must keep every player in sync. Shared files make that easier. All players use the same source file. That lowers the risk of bugs or errors.
Cloud gaming keeps growing. It depends on smart storage to scale up. Single instance systems help meet that demand. They keep the experience fast and stable.
Texture and Asset Management in AAA Games
Big studios manage millions of assets. Textures, sound files, animations, and models all add up. Single instance storage helps studios keep that under control.
Texture Streaming
Many games now stream textures as needed. They don’t load every texture at once. A single version gets streamed, reused, and removed when done.
Asset Linking
Scenes and levels reuse art files. A single rock texture may appear in dozens of spots. The system stores one file and links it each time.
Scene Assembly
During cutscenes or battles, many effects work together. Instead of loading them all fresh, the game grabs shared versions. This keeps the system smooth.
AAA games like Red Dead Redemption 2, Assassin’s Creed, and Horizon Zero Dawn rely on this logic. It’s not visible to players. But it shapes the feel of the entire game.
Keeping Game Assets Safe: File Integrity in Single Instance Systems
Storing one file and linking it many times sounds risky. What if that one file breaks? Game systems have tools to protect against this.
Most engines use backups or version control. If a file is damaged, the system restores a clean copy. This keeps the game stable.
Linking one file also helps developers avoid mistakes. They do not need to fix the same bug in many places. One change updates the whole game.
It also reduces human error. If every scene used a different file, mistakes would grow fast. Single instance models keep everything clean and linked.
Game studios also test each asset before shipping. That test ensures the file loads across every scene without failure. This makes single instance systems both safe and smart.
Single Instance Store vs Deduplication in Gaming: Key Differences You Should Know
Some people confuse a single instance store with deduplication. Both aim to reduce storage waste, but they work in different ways. Let’s break them down.
What Is Deduplication?
Deduplication scans storage blocks for repeating data. It deletes extra copies and leaves one behind. Then, it adds pointers to that copy from other locations. This happens after storage or during backup.
In gaming, deduplication can cut patch sizes or backup folders. It’s used more in cloud systems or file backups than in game engines.
What Is Single Instance Storage?
Single instance storage avoids creating extra copies in the first place. It’s proactive. The system keeps one copy and links to it during asset design or level creation.
In engines like Unreal or Unity, this logic happens during development-not after storage fills up.
Key Differences
| Feature | Deduplication | Single Instance Store |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | After data is stored | During design and runtime |
| Method | Scans and deletes duplicates | Stores one copy, links to it |
| Usage in Gaming | Backup, patch, cloud sync | Core engine and asset loading |
| Efficiency | Good for clean-up | Better for real-time performance |
Both are useful. But for game speed, load time, and dev control, single instance storage offers more direct gains.
Cloud Gaming and Single Instance Store: Is This the Future of Lightweight Games?
Cloud gaming continues to grow. Platforms like NVIDIA GeForce NOW, Xbox Cloud, and Amazon Luna deliver full games over the internet. Players do not install large files locally.
This new model increases the need for smarter storage. Here’s why single instance systems help:
Lower Server Load
Cloud services run games for thousands of users. A single copy of each file used across players keeps the server lighter. This reduces storage costs and boosts speed.
Shared Asset Pools
Games on the cloud often rely on shared environments. A central file pool with single-instance linking lets many titles reuse data without bloating.
Faster Updates Across Systems
Cloud games must update quickly. A system that only updates changed files, not full copies, cuts time and risk of errors. Players get smoother service.
Support for Streaming Assets
Some services stream textures or effects based on player actions. Pulling from a single source speeds up delivery and reduces lag.
As more users adopt cloud play, storage models will need to keep pace. The single instance store will become a core part of that shift.
Future of Smart Storage: AI, Procedural Worlds, and File Management
Games keep changing. New tech brings new needs. AI tools and procedural worlds now shape how data gets stored.
Many games now use AI to generate textures or voice lines. These files can still link to base templates stored once. This keeps game folders light even with complex assets.
Procedural generation creates levels on the fly. These levels still reuse rules, shapes, and base textures. One core set of files supports endless maps. That fits the single instance model well.
Game studios also use machine learning to manage files. These tools scan storage, spot waste, and rebuild scenes with shared links. This makes large game builds cleaner and faster.
As AI gets smarter, storage systems must keep up. Single instance storage already fits this future. It will only grow more useful with time.
Explore More on GameHunt360
Want to learn how modern games work behind the scenes? Check out more guides on GameHunt360:
- Bengtie Gaming Gear: Full Guide and Honest Review
- How to update Minecraft Forge Server: Here is Complete Guide
- Best Xbox Username Generator Tools to Try in 2025 (Safe & Free)
- How to Fix the Request Failed Due to a Fatal Device Hardware Error on Your Device
These guides help you go deeper into game performance, tools, and design choices. Start your journey into smarter game development now.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does “single instance” mean in gaming?
It means storing one copy of a game asset-like a model or sound-and linking to it whenever needed. Instead of saving many copies, the system uses one shared version.
Is this used in all games?
Not all, but most modern games use it in some way. AAA titles, open-world games, and multiplayer platforms often rely on this to manage size and performance.
How does it help game speed?
It cuts down memory use and load time. When the system loads fewer files or references one version many times, it works faster and smoother.
Can it reduce patch sizes?
Yes. If a shared file changes, only that single file updates. This keeps patch sizes small and saves bandwidth for players.
Is this the same as caching?
No. Caching stores data temporarily. Single instance storage is about how assets are built and linked. It’s a permanent part of the game structure.
Does it help with mobile games?
Yes. Mobile games have tight storage limits. Using single-instance files helps keep app size small and updates light.
Conclusion
Why It Matters for Gamers and Developers Alike
Single instance storage may sound technical, but its impact is clear. It helps build better games and it speeds up play and it saves time, money, and space.
Gamers see faster load times, smaller patches, and smoother updates. Developers work faster, fix fewer bugs, and ship leaner products.
This system keeps one version of each file and uses it wisely. It cuts clutter, reduces delays, and keeps the whole game structure clean. Whether in large open-worlds, cloud streaming, or mobile apps, the benefits add up.
As games grow bigger and smarter, storage must grow too. Single instance systems lead that change. They form the quiet backbone of great performance. The next time your game loads fast or updates quick, remember-there’s a good chance this tech made it happen.
Disclaimer: This post shares general information for educational use. It does not include official data from any game studio or developer. All examples and names are used only to explain the concept clearly. Readers should verify details before applying them in professional or technical work.